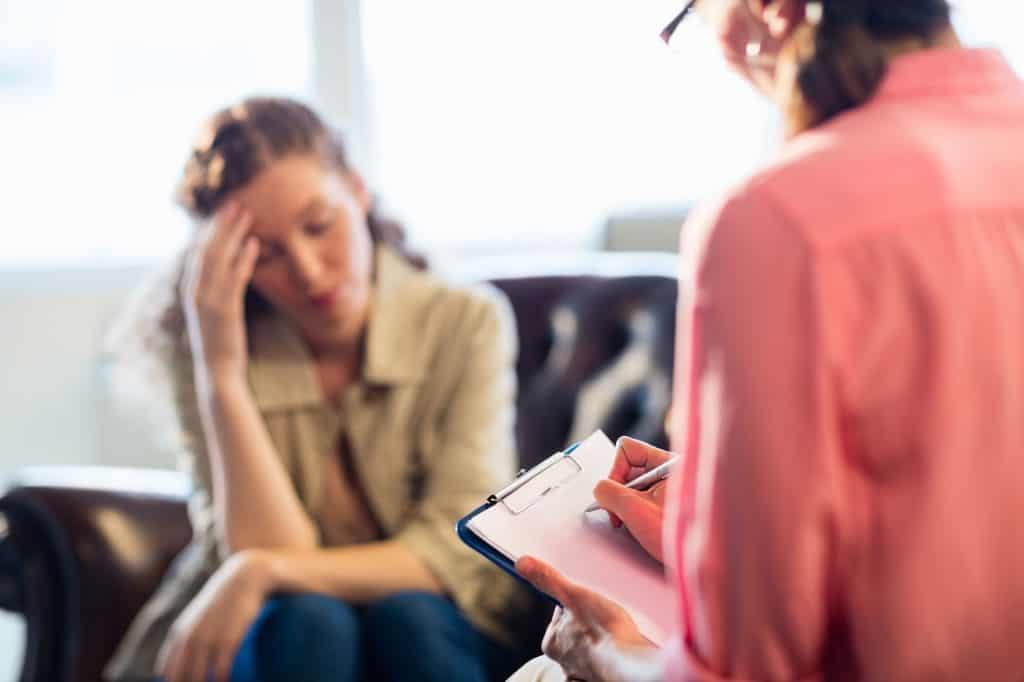
What are the 17 symptoms of PTSD?
Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder (PTSD) is a debilitating mental health condition affecting millions worldwide. It can develop after experiencing or witnessing a traumatic event, impacting one’s emotional and psychological well-being. Therefore, understanding and recognizing the symptoms of PTSD is crucial for both individuals suffering from the disorder and those around them.
In this article, we will delve into the definition of PTSD, examine its prevalence and impact on individuals, and shed light on the importance of identifying and comprehending the 17 symptoms that often accompany this disorder.
Understanding PTSD Symptoms
A psychological condition known as post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD) significantly affects a person’s mental and emotional health. Mental health professionals use the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (DSM-5) to diagnose PTSD because it offers detailed criteria and recommendations. This article will delve into the DSM-5’s criteria for diagnosing PTSD and examine how the symptoms are divided into four major clusters.
- Exposure to Trauma: The individual must have experienced, witnessed, or been confronted with an event involving actual or threatened death, serious injury, or sexual violence.
- Intrusion Symptoms: This cluster focuses on the re-experiencing of the trauma. Symptoms include recurrent and distressing memories of the event, flashbacks, nightmares, and intense psychological or physiological reactions to triggers associated with the trauma.
- Avoidance Symptoms: Individuals with PTSD often attempt to avoid any reminders or triggers related to the traumatic event. This can manifest as avoiding conversations, thoughts, places, people, or activities that may elicit distressing memories or emotions. They may also experience difficulty recalling or discussing significant aspects of the trauma.
- Negative Cognition and Mood Symptoms: This cluster involves persistent negative beliefs or expectations about oneself, others, or the world. It includes feelings of guilt, shame, fear, diminished interest in previously enjoyed activities, and detachment from others.
- Arousal and Reactivity Symptoms: This cluster encompasses heightened states of arousal and reactivity that persist long after the traumatic event. Symptoms may include irritability, outbursts of anger, reckless behavior, hypervigilance, difficulty concentrating, and sleep disturbances.

Intrusive Symptoms
Living with post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD) can be an incredibly challenging experience. One of the hallmark features of PTSD is the presence of intrusive symptoms, which can create a constant sense of distress and disturbance in the lives of those affected. In this blog post, we will explore the four critical intrusive symptoms associated with PTSD: recurrent distressing memories, flashbacks and re-experiencing traumatic events, disturbing dreams related to the trauma, and psychological and physiological reactions to trauma reminders.
Recurrent Distressing Memories
PTSD can cause individuals to relive the traumatic event through distressing memories frequently. These memories can manifest as intrusive thoughts, images, or sensations that disrupt daily life. Whether triggered by external cues or emerging spontaneously, these memories evoke intense emotions and may result in heightened anxiety, fear, or distress.
Flashbacks And Re-Experiencing Traumatic Events
Flashbacks are vivid and overwhelming experiences when individuals feel like they are reliving the traumatic event. Trauma reminders, such as sights, sounds, smells, or even specific thoughts or emotions, can trigger them. During a flashback, individuals may lose touch with their present surroundings and become fully immersed in the traumatic event, as if it is happening in real time.
Disturbing Dreams Related To The Trauma
Another intrusive symptom commonly experienced by individuals with PTSD is the occurrence of distressing and vivid dreams related to the traumatic event. These dreams often involve reenactments of the trauma or variations and can be accompanied by intense emotions like fear, sadness, or anger. Waking up from such dreams can leave individuals feeling exhausted, anxious, and emotionally drained, making it difficult to get restful sleep.
Psychological And Physiological Reactions To Trauma Reminders
Trauma reminders can trigger various psychological and physiological reactions in individuals with PTSD. These reminders can be external, such as specific locations, smells, or sounds associated with the trauma, or internal, such as particular thoughts or emotions. When exposed to these reminders, individuals may experience heightened anxiety, panic attacks, increased heart rate, sweating, or even physical sensations resembling those felt during the traumatic event.
Avoidance Symptoms
Living with post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD) can be daunting and complex. One of the hallmark clusters of symptoms experienced by individuals with PTSD is avoidance. This article will delve into the various avoidance symptoms that can arise, including efforts to suppress thoughts and conversations related to the trauma, avoiding triggers associated with the trauma, difficulty recalling or discussing the trauma, and emotional detachment and loss of interest in previously enjoyed activities. By understanding these avoidance symptoms and their impact, individuals and their loved ones can better navigate the healing process and find strategies to reclaim a fulfilling life beyond trauma.
Efforts To Avoid Thoughts, Feelings, Or Conversations Related To The Trauma
When confronted with the distressing memories of the traumatic event, individuals with PTSD often develop coping mechanisms to avoid engaging with them. This may involve consciously pushing away intrusive thoughts, numbing emotional responses, or actively steering conversations away from the topic of the trauma. Unfortunately, while these avoidance strategies may provide temporary relief, they can hinder the processing and resolution of the traumatic experience in the long term.
Avoidance Of People, Places, Or Activities Reminiscent Of The Trauma
Avoiding reminders of the trauma is a typical response among individuals with PTSD. They may find themselves avoiding certain people, places, or activities that trigger distressing memories or emotions associated with the traumatic event. For example, a car accident survivor might avoid driving or refuse to visit the location of the accident. While avoidance may offer a sense of control, it can also limit one’s ability to engage fully in life and hinder the desensitization process necessary for recovery.
Difficulty Recalling Or Discussing Significant Aspects Of The Trauma
The impact of trauma on memory can manifest as fragmented or distorted recollections of the traumatic event. Many individuals with PTSD struggle to recall specific details or significant aspects of what happened to them. Discussing the trauma may evoke overwhelming emotions or trigger distressing sensations, leading to avoidance. This difficulty in articulating and sharing the experience can hinder healing and strain interpersonal relationships.
Detachment From Others Or Anhedonia (Loss Of Interest In Previously Enjoyed Activities)
PTSD can bring about emotional detachment and a pervasive disconnection from others. Individuals may withdraw from social interactions, experiencing a diminished interest in connecting with loved ones or engaging in activities they once found pleasurable. Anhedonia, the loss of interest or satisfaction in activities, hobbies, and relationships, can exacerbate feelings of isolation and contribute to emptiness and despair.
Negative Cognition And Mood Symptoms
Post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD) can be a challenging experience, with negative cognition and mood symptoms playing a significant role in shaping an individual’s perception of themselves, others, and the world. Therefore, understanding these symptoms is essential for individuals with PTSD and their support systems to provide adequate support and promote healing.
PTSD is characterized by persistent negative beliefs or expectations about oneself, others, and the world. These beliefs can lead to general mistrust and suspicion of people and the world, leading to a loss of faith in abilities, confidence, and self-esteem.
Distorted blame is a common negative cognition symptom seen in PTSD. Individuals may blame themselves excessively for the trauma or its aftermath, even when the blame is unfounded or irrational. This can lead to anger, guilt, and a distorted perception of relationships, making it difficult to rebuild trust and establish healthy connections.
Negative emotional states like fear, anger, and guilt characterize PTSD. Anxiety is prevalent, as individuals may feel on edge and hypervigilant. Anger is a common emotion arising from a sense of injustice or as a way to cope with the overwhelming emotions associated with trauma. Finally, guilt is a complex emotion that individuals with PTSD may grapple with, blaming themselves for their actions or inactions during the traumatic event.
Arousal And Reactivity Symptoms
Arousal and reactivity symptoms are critical to post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD). These symptoms can significantly impact an individual’s daily life, relationships, and well-being. In this blog post, we will explore the four common arousal and reactivity symptoms associated with PTSD: irritability, outbursts of anger or aggressive behavior, reckless or self-destructive behavior, hypervigilance-triggered startle responses, and problems with concentration and sleep disturbances.
Irritability, Outbursts Of Anger, Or Aggressive Behavior
Individuals with PTSD may experience heightened irritability, making them easily agitated or provoked. They may also struggle with managing their anger, leading to frequent outbursts or aggressive behavior. In addition, even minor stressors can trigger intense emotional reactions, making it challenging for them to regulate their emotions effectively.
Reckless Or Self-Destructive Behavior
PTSD can manifest in self-destructive behaviors as individuals engage in reckless activities or take unnecessary risks. These behaviors may serve as a coping mechanism or an attempt to regain control over their lives. Examples include substance abuse, dangerous driving, or engaging in high-risk activities without considering the consequences.
Hypervigilance And Exaggerated Startle Response
Hypervigilance is a state of constant alertness and heightened sensitivity to potential threats. Individuals with PTSD may always be on guard, scanning their environment for signs of danger. As a result, they may experience an exaggerated startle response, where even small or unexpected stimuli can trigger a strong physical and emotional reaction. This hyperarousal can be exhausting and make it difficult for individuals to relax or feel safe.
Problems With Concentration And Sleep Disturbances
PTSD can significantly impair an individual’s ability to concentrate and focus on tasks. As a result, they may need help staying present and find their minds wandering or becoming easily distracted. Additionally, sleep disturbances are common, with individuals experiencing insomnia, nightmares, or recurring disturbing dreams. A lack of restful sleep can further exacerbate other symptoms and negatively impact overall functioning.
The Impact Of Ptsd Symptoms
Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder (PTSD) can profoundly impact individuals, affecting multiple aspects of their lives. Understanding these impacts is essential to supporting and fostering empathy for those with PTSD. This blog post will explore the far-reaching consequences of PTSD symptoms and shed light on the challenges individuals face in personal relationships, social interactions, occupational, and academic settings, as well as the increased risk of comorbid mental health disorders and physical health consequences.
Challenges In Personal Relationships And Social Interactions
PTSD symptoms can have a significant impact on personal relationships and social interactions. For example, avoidance, emotional detachment, and irritability can hinder effective communication and lead to misunderstandings or conflicts. In addition, trust issues may arise as individuals struggle with recurrent distressing memories or hypervigilance, making engaging in social activities and experiences difficult. This can lead to feelings of isolation, misunderstanding, and strained relationships with friends, family, and romantic partners.
Occupational And Academic Difficulties
PTSD can significantly impact an individual’s occupational and academic pursuits. It can interfere with their ability to focus on tasks, meet deadlines, and maintain productivity. Negative thoughts and emotions can affect motivation and the enjoyment of work or studies. Hypervigilance and exaggerated startle responses can make feeling safe and comfortable in a position or educational environment challenging. Individuals with PTSD may struggle with absenteeism, presenteeism, or difficulty adapting to workplace or academic demands, potentially hindering career advancement and academic success.
Increased Risk Of Comorbid Mental Health Disorders
Other mental health disorders like depression, anxiety, substance abuse, and sleep disorders often accompany PTSD. These comorbidities can exacerbate the symptoms of PTSD and create a complex web of challenges for individuals. Therefore, healthcare providers must address and manage these comorbidities effectively to support individuals in their recovery journey.
Physical Health Consequences And Impact On Overall Well-Being
PTSD can have physical health consequences like cardiovascular problems, gastrointestinal disorders, immune system dysregulation, and chronic pain. Sleep disturbances, such as insomnia or nightmares, further contribute to fatigue and physical discomfort. The combination of psychological distress and physical health consequences can create a vicious cycle where the physical symptoms worsen the psychological symptoms and vice versa. Therefore, it is essential to recognize the interconnectedness of mental and physical well-being in individuals with PTSD and provide comprehensive care.
Understanding the 17 symptoms of PTSD and their significance is crucial to recognizing the far-reaching impact of this disorder. From intrusive memories to avoidance behaviors, negative cognition, and arousal symptoms, PTSD can significantly affect an individual’s life, relationships, and overall well-being. Therefore, it is essential to emphasize the importance of addressing PTSD and seeking support. If you or someone you know is experiencing these symptoms, don’t hesitate to ask for help. Contact us today at 1(602) 641-4617 or visit our website at https://www.corerecoveryaz.com to learn more about our services and how we can support you on the path to healing and recovery. Remember, there is hope; you don’t have to face PTSD alone.