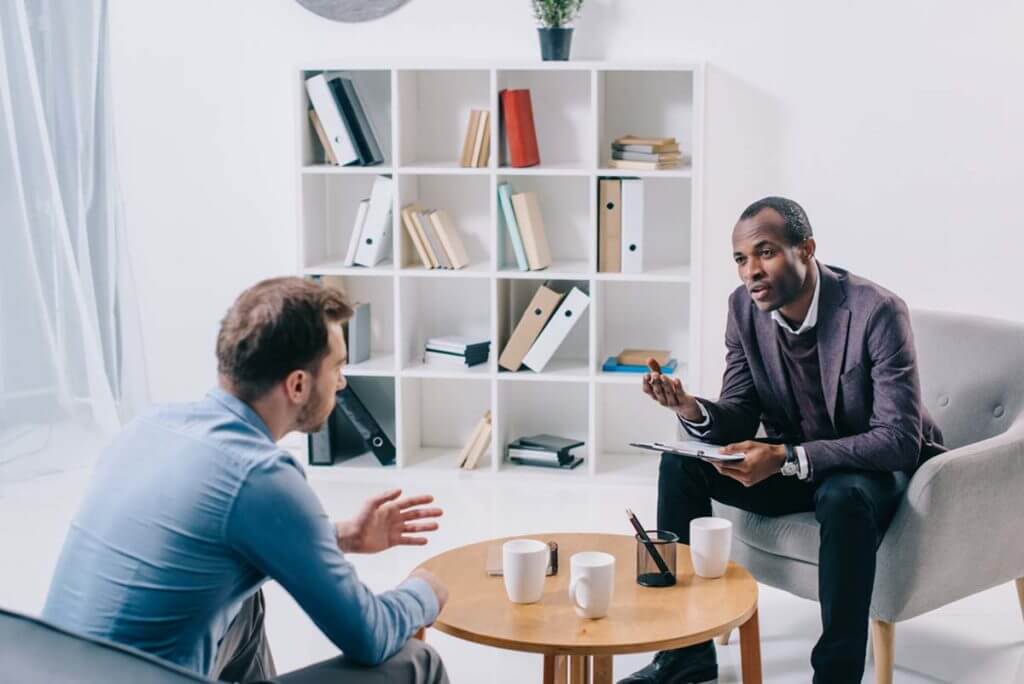
In the complex tapestry of human experiences, trauma is a powerful force that can profoundly impact individuals emotionally, psychologically, and even physically. Trauma, whether resulting from a single distressing event or prolonged exposure to adverse circumstances, can leave deep scars that reverberate throughout a person’s life, affecting their well-being and relationships. Understanding the intricacies of trauma and its far-reaching consequences is crucial in recognizing the importance of seeking therapy for trauma recovery. In this blog, we delve into the definition of trauma, exploring its various forms and the profound effects it can have on individuals. Moreover, we shed light on the transformative role of therapy for trauma, highlighting its significance in fostering healing, resilience, and a path toward reclaiming one’s life from the clutches of past wounds.
What Is Therapy For Trauma Recovery
Therapy for trauma recovery is a specialized and evidence-based approach designed to help individuals heal from the emotional and psychological wounds caused by traumatic experiences. Trauma can stem from various sources, such as accidents, abuse, natural disasters, or witnessing violence. The therapy process involves creating a safe and supportive environment where individuals can explore and process their trauma-related thoughts, emotions, and memories. Techniques like Trauma-focused Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (TF-CBT), Eye Movement Desensitization and Reprocessing (EMDR), and somatic experiencing are commonly used to address trauma’s impact on the mind and body. Therapy for trauma recovery aims to empower individuals, fostering resilience and enabling them to move forward with renewed strength and hope.
The Therapeutic Process In Trauma Recovery
Trauma is a profoundly distressing experience that can have long-lasting effects on a person’s mental, emotional, and physical well-being. It shatters one’s sense of safety and security, leaving behind emotional wounds that may seem impossible. However, there is hope in the form of therapy for trauma recovery, a guided journey toward healing and restoration.
- Building Trust and Rapport: For those who have experienced trauma, trusting others can be daunting. Therapists work diligently to build rapport with their clients, respecting their boundaries and demonstrating genuine care and compassion. As trust grows, survivors become more willing to open up and explore their trauma-related experiences.
- Validating the Trauma Experience: Trauma survivors often grapple with guilt, shame, or self-blame, which can hinder the healing process. In therapy, validation is pivotal in helping individuals acknowledge that their reactions to trauma are normal responses to abnormal situations. Validating the trauma experience helps survivors understand they are not alone in their struggles.
- Trauma-Focused Interventions: Trauma-focused interventions help survivors cope with traumatic memories and emotions through TF-CBT, EMDR, somatic experiencing, and body-based techniques, addressing negative thought patterns, emotional charge reduction, and mind-body connection.
- Working Through Trauma-Related Beliefs: Trauma can significantly impact an individual’s belief systems and worldview. In therapy, survivors examine and challenge these trauma-related beliefs, paving the way for cognitive restructuring and positive self-reappraisal.
- Fostering Resilience and Post-Traumatic Growth: As therapy progresses, survivors rebuild their lives with newfound resilience. Post-traumatic growth becomes possible as individuals develop a deeper understanding of themselves, find meaning in their experiences, and foster personal growth and strength.
- Addressing Individual Needs: Every trauma survivor’s journey is unique, and therapy recognizes this diversity. Therapists tailor their approaches to meet individual needs, considering cultural, personal, and contextual factors that shape the recovery process.
The therapeutic process in trauma recovery is a transformative path toward healing and restoration. Through a safe and supportive environment, trauma-focused interventions, and the cultivation of coping strategies, individuals can confront their traumatic past and find a way to rebuild their lives. Seeking professional help and engaging in therapy for trauma recovery is a courageous step towards reclaiming one’s life and moving towards a future filled with hope and resilience.
Common Challenges Faced By Individuals During Recovery
Recovery from adversity is challenging, especially for individuals with trauma, addiction, or mental health issues. Common challenges arise during the process, but acknowledging and understanding these hurdles can provide valuable insights and support for individuals and their loved ones.
- Dealing with Relapses and Setbacks: Recovery is a complex journey with setbacks, which can be disheartening and lead to feelings of failure or hopelessness. Recognizing and using relapses as learning opportunities can help individuals remain resilient and committed to their recovery goals.
- Managing Triggers and Temptations: During recovery, individuals may encounter triggers or face temptations that remind them of their past behaviors or traumatic experiences. Coping with these triggers and learning healthy ways to manage temptations is essential for maintaining progress and preventing relapses.
- Dealing with Emotions and Mental Health Challenges: Recovery often involves confronting deep-seated emotions and addressing underlying mental health issues. This process can be emotionally draining and overwhelming. Learning to cope with and healthily process emotions is crucial for long-term healing.
- Navigating Relationships and Social Pressures: Family dynamics, friendships, and social environments can impact recovery. Individuals may face pressure to conform to previous behaviors or encounter unsupportive relationships. Setting healthy boundaries and surrounding oneself with a supportive network can be instrumental in maintaining recovery.
- Addressing Stigma and Seeking Social Acceptance: Society’s stigma around addiction, mental health, and trauma can lead to feelings of shame and isolation. Overcoming these societal barriers and seeking acceptance and understanding can empower individuals to embrace their recovery journey without judgment or fear of rejection.
- Finding Motivation and Purpose: As the recovery progresses, individuals may experience moments of doubt or question their motivation for change. Identifying personal values, setting achievable goals, and finding a purpose can reignite motivation and provide a meaningful direction in recovery.
Recovery is a transformative journey requiring resilience, courage, and support. Understanding common challenges can foster empathy, compassion, and appreciation for healing triumphs. Acknowledging these challenges and seeking professional guidance empowers individuals to navigate the path with purpose, determination, and hope. With the right tools and support, recovery becomes a transformative process, empowering individuals to reclaim their lives and embrace a healthier future.
Techniques Used In Trauma Recovery Therapy
Trauma can leave deep scars on a person’s psyche, impacting their emotional well-being and overall quality of life. However, therapy offers hope for those seeking healing and restoration from traumatic experiences. Skilled therapists employ various evidence-based techniques tailored to each individual’s needs, facilitating the journey toward trauma recovery. Let’s delve into some of the powerful techniques used in therapy for trauma recovery:
Trauma-focused Cognitive-Behavioral Therapy (TF-CBT)
TF-CBT is a widely used and practical approach that targets the negative thought patterns and beliefs stemming from trauma. Individuals can gain a fresh perspective on their trauma-related experiences by identifying and challenging these negative thoughts. Additionally, TF-CBT helps address and process the intense emotions associated with the trauma, fostering emotional regulation and coping skills.
Eye Movement Desensitization and Reprocessing (EMDR)
EMDR is a unique and proven method for processing traumatic memories. Individuals can access and reprocess distressing memories in a safe environment through guided eye movements or other forms of bilateral stimulation. This reprocessing reduces the emotional charge of the memories, allowing individuals to integrate them more healthily and adaptively.
Somatic Experiencing and Body-Based Interventions
Trauma is not only stored in the mind but also in the body. Somatic experiencing recognizes the mind-body connection and facilitates the release of stored trauma through physical exercises and techniques. By gently engaging with bodily sensations and movements, individuals can discharge trapped energy, promoting release and grounding.
Narrative Therapy and Storytelling
Narrative therapy encourages individuals to share their trauma narrative in a supportive, non-judgmental space. By externalizing their experiences through storytelling, survivors can gain a sense of agency over their own stories. This process helps reframe the trauma experience, empowering individuals to view themselves as resilient protagonists rather than helpless victims.
Mindfulness and Relaxation Techniques
Mindfulness practices, such as meditation and deep breathing exercises, are invaluable for managing trauma-related anxiety and distress. By staying present at the moment, individuals can observe their thoughts and emotions without judgment, reducing their reactivity to trauma triggers. Relaxation exercises also play a significant role in promoting emotional well-being and providing relief from the heightened stress that often accompanies trauma recovery.
Trauma recovery therapy is a personalized process involving various techniques, such as TF-CBT, EMDR, and somatic experiencing. Narrative therapy and mindfulness empower survivors, reframing experiences and cultivating emotional resilience. With skilled guidance and dedication, these techniques can lead to profound transformation and a brighter future.
Self-Help Strategies For Trauma Survivors
Traumatic experiences significantly impact individuals’ mental, emotional, and physical well-being. Professional help and therapy are crucial for recovery, but self-help strategies can foster healing, resilience, and personal growth. These tools empower survivors to navigate challenges and actively participate in their healing journey.
- Practice Mindfulness: Mindfulness is a powerful tool for trauma survivors to manage overwhelming emotions and anxiety. Practices like meditation and deep breathing exercises help individuals become more aware of their thoughts and emotions, enabling them to respond more groundedly to triggers and stressors.
- Engage in Creative Expression: Art, writing, music, and other forms of creative expression can be outlets for processing emotions and trauma-related experiences. Engaging in creative activities can help survivors express their feelings and gain insights into their healing process. It offers a safe space for exploring emotions that may be challenging to verbalize.
- Connect with Supportive Relationships: Trauma survivors need a supportive network of understanding, compassionate individuals to feel connected and encouraged during recovery. Openly sharing experiences with trusted individuals fosters deeper connection and healing.
- Set Boundaries and Prioritize Self-Care: Trauma survivors face increased stress sensitivity, so setting healthy boundaries and prioritizing self-care activities like exercise, healthy eating, and rest are crucial for emotional well-being and healing.
- Seek Professional Support When Needed: Seeking professional support is crucial for trauma recovery, as qualified therapists and mental health professionals offer specialized guidance, tailor interventions, and provide a safe space for exploring trauma-related issues.
Trauma survivors can benefit from self-help strategies, such as mindfulness, creative expression, support networks, and stress management, to foster resilience, personal growth, and healing. Combining these tools with professional support and therapy is essential for a comprehensive approach to trauma recovery.
Trauma survivors often face immense emotional distress and struggle to cope with the lasting impact of traumatic experiences. The burden of trauma can lead to anxiety, depression, and feelings of isolation, hindering individuals from living fulfilling lives.
Without effective intervention, the trauma’s effects may continue to dominate survivors’ thoughts and emotions, hindering their ability to move forward. Reliving traumatic memories and negative thought patterns can perpetuate a cycle of distress and prevent the healing process.
In therapy for trauma recovery, a range of powerful techniques is employed to help survivors regain control of their lives and foster emotional healing. Trauma-focused cognitive-behavioral therapy (TF-CBT) helps challenge negative thought patterns and address trauma-related beliefs. Eye Movement Desensitization and Reprocessing (EMDR) facilitate processing of traumatic memories, reducing emotional intensity. Somatic experiencing and body-based interventions recognize the mind-body connection, allowing the release of stored trauma through physical exercises. Narrative therapy and storytelling empower survivors to reframe their trauma experiences, and mindfulness techniques provide tools for managing anxiety.